Tokenization of Bonds: A Catalyst for Wider Retail Participation and Deeper Capital Markets

Tokenization has emerged as a game-changer in the financial world, unlocking new possibilities for various asset classes. Among these, the tokenization of bonds is rapidly gaining traction, revolutionizing the capital market landscape. By digitizing traditional bonds and transforming them into blockchain-based tokens, this innovative approach offers a plethora of benefits, including increased accessibility for retail investors and enhanced market depth for companies seeking capital. In this article, we will explore how the tokenization of bonds can revolutionize the capital market, fostering greater participation from retail investors and facilitating better financing options for businesses.
Understanding Tokenization of Bonds
Traditionally, bonds have been a popular investment instrument for both retail and institutional investors. A bond represents a debt instrument issued by governments, corporations, or other entities to raise capital. The issuer promises to pay back the bond's face value along with periodic interest payments until maturity. However, traditional bond investments often come with certain limitations, including high minimum investment requirements, limited liquidity, and geographical restrictions.
Tokenization introduces a transformative solution by representing bond ownership through digital tokens on a blockchain. Each token corresponds to a fraction of the bond's value and terms, allowing investors to buy and sell these tokens, rather than whole bonds, on digital asset exchanges. This opens up the bond market to a broader range of participants, paving the way for retail investors to invest in traditionally inaccessible assets and enabling companies to attract diverse sources of capital.

Revolutionizing the Capital Market for Retail Investors
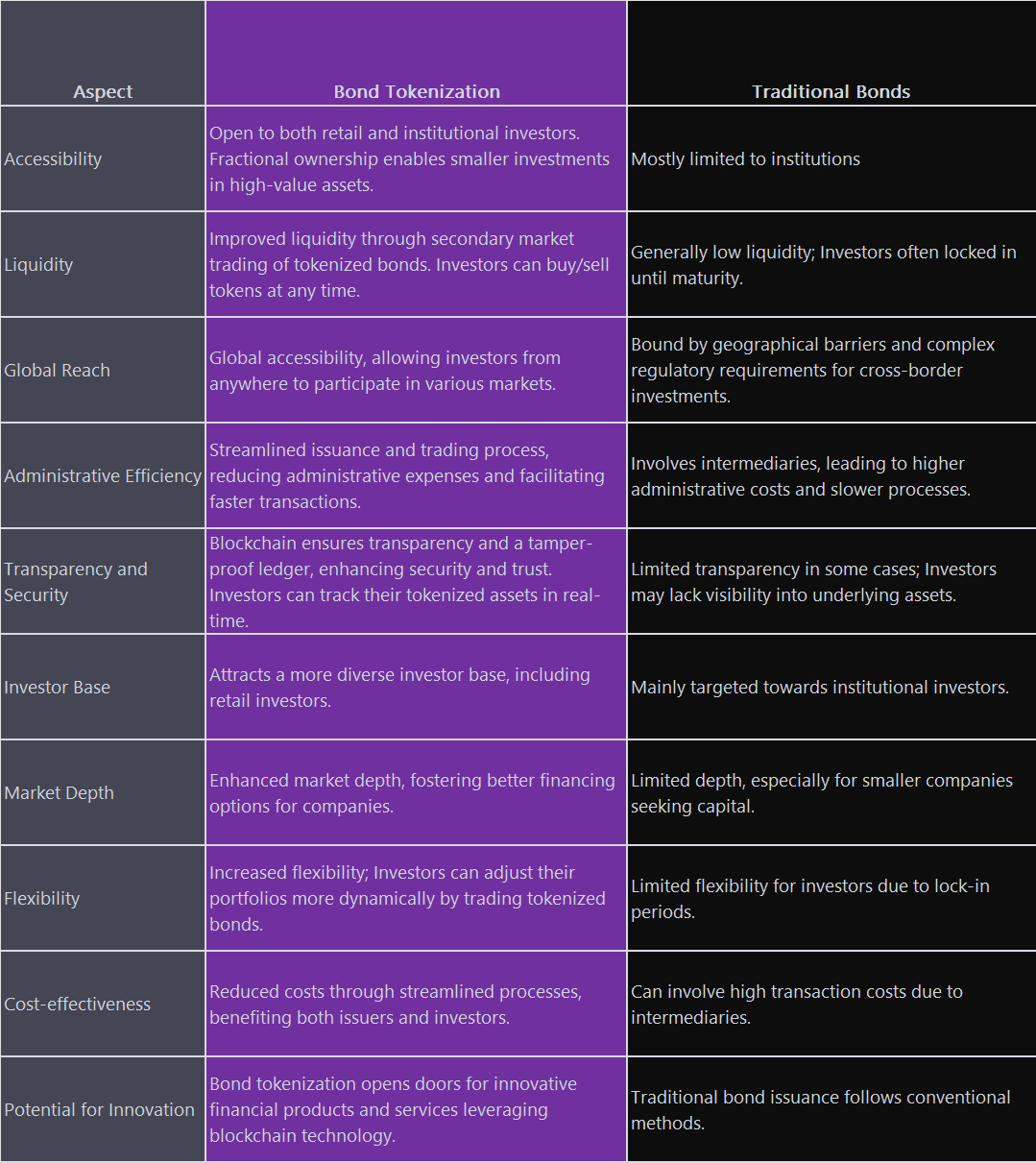
- Accessibility and Fractional Ownership: Tokenization allows retail investors to participate in the bond market with smaller investment amounts. By breaking bonds into fractional tokens, investors can buy portions of bonds that were previously out of reach due to high minimum investment thresholds.
- Enhanced Liquidity: Tokenized bonds can be traded on secondary markets, making them more liquid than their traditional counterparts. Investors can buy and sell tokens without waiting for the bond's maturity, providing greater flexibility and exit options.
- Global Investment Opportunities: Tokenization transcends geographical barriers, enabling retail investors from all corners of the world to invest in a wide range of bonds issued by various entities. This fosters a more inclusive and global investment landscape.
- Cost Efficiency: Traditional bond transactions often involve intermediaries, leading to higher costs for investors. Tokenization streamlines the process, reducing administrative expenses and making bond investments more cost-effective.
Facilitating Deeper Capital Markets for Companies
- Access to Diverse Investor Base: Tokenized bonds attract a broader range of investors, including retail and institutional participants. This expanded investor base allows companies to diversify their funding sources and reduce reliance on traditional channels.
- Improved Market Efficiency: Tokenization enhances transparency and reduces administrative burdens associated with bond issuance and trading. This efficiency benefits both issuers and investors, making the market more attractive to all parties.
- Lower Barriers to Entry: Smaller companies or startups seeking capital can use tokenized bonds to raise funds without the complexity and costs associated with traditional debt instruments. This democratizes access to capital markets and fosters entrepreneurship.
- Increased Market Depth: As tokenized bonds gain popularity, the overall depth and liquidity of the capital market are likely to improve. This heightened market activity can further incentivize companies to consider tokenized bonds as a financing option.
Regulatory Considerations and Challenges
Despite the immense potential of tokenized bonds, regulatory considerations and challenges need to be addressed. Regulators must establish clear guidelines to ensure investor protection, prevent market manipulation, and facilitate compliance with existing financial regulations.
Conclusion
The tokenization of bonds represents a significant leap forward in the evolution of capital markets. By providing wider access to retail investors and facilitating greater market depth for companies, tokenized bonds offer a win-win solution for both investors and issuers. The digitization of assets not only opens up new investment opportunities for retail investors but also presents a more efficient and inclusive financing option for companies. As regulatory frameworks continue to evolve to accommodate this burgeoning technology, we can expect to witness a thriving ecosystem of tokenized bonds driving the future of finance.

